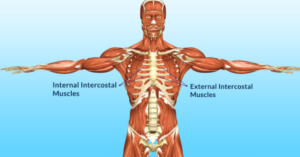
An intercostal muscle strain occurs when the muscle stretches, pulls or is partially torn. Your intercostal muscles are several groups of muscles that run between the ribs.
These muscles help form and move the chest wall. They are involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing. They expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity to facilitate breathing.

A strain in any of the layers of these muscles can cause pain and difficulties in breathing. For most people, muscles strain are a common cause of chest pain. Studies show that 21 to 49% of musculoskeletal chest pain comes from the intercostal muscles.
This article offers an insight into the meaning, causes, symptoms, treatment and healing time of intercostal muscles strain. There are three layers of intercostal muscles: the external intercostal, the internal intercostal and the innermost intercostal.
Intercostal muscle strain NHS
According to NHS, sprain and strain are common injuries that affect muscles and ligaments. These injuries normally occur when playing sports. They can occur when you suddenly change direction, speed suddenly, fall or collide with an object or person.
NHS adds that a sprain will occur when one or more ligament has been stretched, twisted or torn. This will often occur as a result of excessive force being applied to a joint. A strain, on the other hand, occurs when the muscle fibers stretch or tear.
Through common in the legs and back, stains can occur on any muscles of the body. A muscle strain is usually the result of the muscle being stretched beyond its limits. It can also occur as a result of the muscle being forced to contract too quickly.
Intercostal muscle strain from coughing
As mentioned, an intercostal muscle strain will often occur as a result of a tear in the muscle between the ribs. The pain and tear can be a result of chronic coughing or sneezing.
Coughing can cause a sudden contraction of the muscle especially in cases where the muscles are not in the right proper position when coughing. According to mayo clinic, a cough is your body’s way of responding to an irritant in your throat or airways.
They add that an occasional cough is normal and healthy but if it persists for several weeks or brings up bloody mucus, it can be a sign of something serious. You will need to have it checked out by your doctor as soon as possible.
What causes intercostal muscles strain?
As said, a muscles stain occurs when you stretch, pulls or partially tear the muscles. You can pull or strain the intercostal muscle in many different ways. In most cases, these muscles are usually hurt during twisting motion.
The pain can start either from a sudden injury or begin gradually from repetitive motion. You are likely to strain your chest muscles when performing the following activities:
- Heavy lifting while twisting upper body. this puts a lot of strain on your intercostal rib cage that can cause them to tear and become very painful
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- In sports such as tennis, rowing, or golfing
- Falling
- Trauma in the ribcageexample when in a car accident
- Slipping rib syndromethis is a condition in which the cartilage on the lower ribs moves, causing pain in the chest and upper abdomen.
- Sitting for long in an incorrect posture can also strain your ribcage muscle. This is why wrong sitting posture can cause muscle tightness and painful feeling in your back just below the shoulder blade.
Intercostal muscle strain symptoms
Regardless of what the cause of the strain is, there some signs and symptoms that can help identify and intercostal muscle strain. They include:
- A sharp pain around the ribcage at the time of the injury. This pain can also come on more gradually. The pain worsens when you twist, stretch or inhale deeply, sneeze or when you cough.
- A torn muscle may also become inflamed or swollen. It is possible to notice some swelling between and around the affected ribs
- The area of the stain between your ribs may feel sore or tender
- After a muscle strain, the injured muscle may fell tight when breathing, twisting or when reaching for something.
- Bruising or redness around the affected ribs
- Muscle spasms are likely symptoms of a muscle strain
- Weakness and loss of function, this can make it hard and painful to breathe
- Upper back pain
Most of the symptoms above may be similar to those caused by a more serious condition. To prevent any complication, we recommend you schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. He or she will be able to assess the symptoms and identify what the underlying cause might be.
Intercostal muscle strain pain left side
Apart from an intercostal muscle strain, pain on the left side can be a sign of costochondritis, a condition marked by the inflammation of the junction where the upper ribs join with the cartilage that holds them to the breastbone.
Costochondritis causes localized chest pain that reproduces by pushing on the cartilage in the front of your ribcage. This condition is relatively harmless and will often clear without treatment. The actual cause is unknown but may occur from increased activities involving the arms.
Another common cause of pain on the left side if rib fracture. In other cases, the left pain can also be referred from organs located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. Other likely cause of the left pain would include the following:
- Acid reflux disease characterized by the backflow of the gastric juices to the esophagus
- Digestive ailments
- Pneumothorax or collapsed lung occurs when air is present in the pleural space (two-layered structure that comprises the parietal pleura that covers the inner chest wall)
Intercostal muscle strain healing or recovery time
The recovery time of a muscle strain will often depend on different factors. For starters, how fast or slow the muscle strain heal May depend on:
- How sever the strain was
- The extern of muscle affected
- The general health of the affected person
- The treatment prescribed among others
With proper treatment and physical therapy, it could take 2-3 weeks to relieve the symptoms of moderate intercostal muscle strain fully. For severe injuries, it may take up to 2 months for the strain to complete heal.
While treating the strain, you will be required to avoid twisting and reaching activities that can worsen the pain and prolong the recovery time.
Intercostal muscle strain treatment
According to NHS, minor cases of intercostal muscles strain can usually be treated with simple self-care techniques such as protection, rest, ice, compress and elevation also known as RICE therapy. However, if you feel like you have injured the muscle, you may need to see your doctor as soon as possible.
A proper medical examination will help identify which muscle has been strained. Your doctor will also ensure that no other structure in your chest has been affected before the right treatment option can be prescribed.
In most cases, you can use the following to treat and ease the symptoms of intercostal muscle strain:
1. Cold compress
According to health line, cold therapy can help ease pain and relieve inflammation of a muscle strain. Simply apply a cold compress over the affected area 30 minutes at a time several times a day. You can choose to use an ice pack or a gel cold pack.
2. Hot compress
After two days of applying a cold compress, you may want to shift to a hot compress now. While a cold compress will help ease the pain and swelling, a hot compress will help loosen and relax the muscle.
Use a heating pad to apply the compress 30 at a time. An alternative would be to use a warm damp face towel. You can also add two tablespoons of Epsom salt and soak your body in it. Magnesium is an important mineral for muscle function.
3. over the counter pain medication
At home, over the counter medication such as anti-inflammatories and painkillers may help ease the symptoms of intercostal muscles strain including the severe pain and swelling in and around the ribcage.
When using OTC drugs make sure to follow the directions on how much how often the medicine should be used. It is important to consult with your doctor before using most of these drugs.
4. Ginger
When treating a swollen intercostal muscle, eating ginger has been found to help relieve inflammations between ribs. Apart from bringing down the swelling, it can also help soothe the pain and other symptoms caused by a muscle strain.
5. Breathing exercises
Breathing exercise can also be an effective way to treat intercostal muscle strain. Breathing with a muscle strain can be very painful, the downside is, taking shallow breath instead of full, deep breathes can lead to infection.
Deep breathing is therefore required, this is what you will need to do:
- Hold a pillow against your injured muscle
- Breath in slowly and as deeply as you can
- Hold the breath for some seconds
- Now breath out slowly
- Repeat this at least 10 times every 5 hours
6. Muscle relaxants
In cases of severe pain, muscle relaxants may be used to reduce painful muscle tension. Muscles relaxants are prescribed by a healthcare practitioner, they work as a depressant on the central nervous system to real the muscles.
They are only to be used for a short-term
7. Deep muscle massage
You could also apply a deep muscle massage to ease the symptoms of an intercostal muscle strain. A deep massage is said to increase blood flow to the injured area. This can help increase the flexibility in the muscle, ligament, and tendons.
Have a professional chiropractor apply the message. He or she will also focus on easing the surrounding muscles that may have been affected by an injury or trauma.
Intercostal muscle strain exercises video
Intercostal muscle strain exercises
Apart from treatment, there are some exercises that can help strengthen your back and upper body. Depending on the severity of muscle strain, gentle physical therapy may be recommended to stretch the tender muscle.
Common intercostal muscle strain exercises will include the following:
1. Rotating your upper body
A simple way to strengthen the intercostal muscle is to rotate your upper body. All you need to do is:
- Sit with your arms folded across the chest then
- Gently rotate your upper body from left to right, right to left
- Do this daily until the stain is fully recovered
2. Forward stretch
In this exercise, you are required to do the following:
- Sit on the floor with the left leg straight in front of the body and the right bent so that the sole of the foot touches the knee
- Lean forward as far as you can over the right leg, rotating the torso slightly and touching both palms to the floor
- Once you feel a stretch in the back intercostal muscles on the left, hold the stretch for 30 seconds then do the same on the other side.
3. Gate Pose
Gate pose is a common yoga position that stretches the intercostal ate the side of the torso. This is what you will need to do:
- On comfortable padding, rise up on both knees and extend the right leg straight to the side With the kneecap facing up and the sole on the ground as much as possible
- Extend both arms to the sides, then bend the upper body toward the right such that the right arm rests on the extended leg
- Continue to reach the left arm overhead so that a stretch is felt in the left ribs
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds then repeat on the left side
Reference:
- Intercostal muscle: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intercostal_muscle
- How to identify and treat an intercostal muscle strain: https://www.healthline.com/health/intercostal-muscle-strain
- Treating intercostal muscle strain: https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/upper-back-pain/treating-intercostal-muscle-strain
- Therapy for intercostal muscles: https://www.livestrong.com/article/490733-therapy-for-intercostal-muscles/
- Intercostal muscle strain: https://healthool.com/intercostal-muscle-strain/
- Sprain and strains: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/sprains/Pages/Introduction.aspx






