Fecal incontinence can affect all aspect of your life greatly, reducing your health, personal and social life. Emotional effects such as stress, anxiety, feeling dirty, poor body image, depression can weigh you down. This can be a symptom of an underlying problem or medical condition. Diarrhea, constipation or weak muscle controlling the opening of the anus are some of the causes. Read more about the causes in adults, child, the symptoms and how to manage with pads and treatment.
Fecal incontinence definition
According to Wikipedia, Fecal incontinence also known as bowel, anal or accidental incontinence is a lack of control over defecation leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements, and mucus or solid feces.
Bowel or fecal incontinence generally, is the inability to control bowel movements. This results in involuntary soiling. Everyone has had their experience, and it can vary from person to person. You may feel a sudden need to use a toilet but you are unable to reach the toilet in time. Some people experience no sensation at all and end up soiling themselves. You may experience slight soiling when passing wind.
Fecal incontinence meaning
What does it mean to experience anal, bowel or fecal incontinence? It is thought one in every 10 people will experience this condition at one point in their life. Anal incontinence is a symptom of an underlying problem or medical condition. As pointed out earlier, many cases are caused by diarrhea, constipation or weakening of the muscles that controls the opening of the anus.
Inability to control bowel movement could also mean you’ve been suffering from a long-term condition such as diabetes, dementia and multiple sclerosis. Read more about the causes in the post. Anal incontinence can be upsetting and a difficult condition to live with. But there are ways to manage and treat this condition. Make sure you see your healthcare provider for diagnosis.
Fecal incontinence symptoms
Fecal incontinence or bowel incontinence is the inability to control bowel movements. The condition ranges from occasional leakages of stool unexpectedly from the rectum to complete loss of bowel control. Common causes of this condition would include diarrhea, constipation, and nerve and muscle damage. Regardless of what the underlying cause of the condition is, you should not shy away from seeking proper health care.
In most people, fecal incontinence is experienced after an occasional bout with diarrhea. Some common symptoms experienced will include the following:
- Accident or fecal leakage especially during episodes of severe diarrhea
- Inability to hold gas
- Abdominal discomfort
- Silent leakage of stool
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
Fecal incontinence causes
There are different causes of fecal incontinence. Some of the causes are more common than the others. Fecal or bowel incontinence is common in adult’s female than in any other group of people. A common cause of the condition is damage to one or both of the anal sphincter muscles. A common cause of anal sphincter damage is childbirth through the vagina.
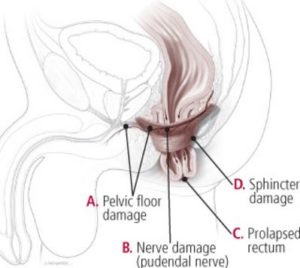
In humans, the external sphincter is responsible for delaying bowel emptying once the rectum fills and the urge to empty the bowel is felt. Having a weak or damaged external sphincter muscle makes one experience urgency, if you can’t reach a toilet in time, you become incontinent. If the damage is to the internal anal sphincter, then you are likely to suffer from passive soiling.
- Muscle injury and damage to the ring of muscles at the end of the rectum, known as anal sphincter makes it very hard to hold stool for long. This is a common cause of bowel incontinence. This damage is common after childbirth.
- Reduce storage capacity in the rectum due to surgery or scarred rectum, it becomes hard for the rectum to stretch and accommodate stool. These can also be caused by radiation treatment or inflammatory bowel disease, this may cause the stool to leak out.
- Nerve damage of the nerves that senses stool in the rectum or those that control the anal sphincter can also lead to fecal incontinence. These kind of nerve damage are common during childbirth, constant straining during bowel movements, spinal cord injuries or stroke.
- Constipation which leads to a mass of dry stool in the rectum may cause the anal muscles to overstretch and eventually weaken. This may allow watery stool from the digestive tract to leak out.
- Diarrhea due to an infection or irritable bowel syndrome is also a common cause of bowel or fecal incontinence.
- Surgery in the rectum or anal area, for example, the done to correct enlarged veins in the rectum or anus or complex operation involving the rectum can cause the muscles to weaken. It can also cause nerve damage which leads to fecal incontinence.
- Rectocele which is a prolapse of the wall between the rectum and the vagina is also a common cause of fecal incontinence.
- Childbirth by vaginal delivery is a common cause of fecal incontinence, especially in first time delivery. This is due to weakened and damaged anal muscles.
- Hemorrhoid also referred to as pile, refers to swollen veins or group of veins in the region of the anus.
- Rectal prolapse is the protrusion of either the rectal mucosa or the entire wall of the rectum. Partial prolapse may involve only the mucosa, it will only protrude by few centimeters. A complete prolapse will involve all the layers of the rectal walls
Fecal incontinence in adult
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, nearly 18 million US adults, about 1 in every 12 have fecal incontinence. Though more common in older adults, nearly anybody can have a bowel control problem. According to statistics, the condition is more common in adult women than men.
The risk of having fecal incontinence in adults increases with having any of the following:
- Diarrhea which is the passing of loose watery stool. Diarrhea is a condition in which feces are discharged from the bowels frequently and in liquid form. This can be as frequent as five times a day.
- Urgency, or the sensation of having very little time to get to the toilet for a bowel movement.
- In adult females, a difficult childbirth with injuriesto the pelvic floor, the muscles, ligaments, and tissues that support the uterus, vagina, bladder and rectum can all lead to fecal incontinence.
- Having a disease that damages the nervous system is another risk factor for developing bowel incontinence
- Poor overall health from multiple chronic or long-lasting illness is the other common risk factor of developing this condition.
Fecal incontinence in child
Though common in adult, fecal incontinence can also be experienced in children. In children, stool incontinence is the voluntary or involuntary passage of stool in inappropriate places. Encopresis is a common cause of constipation in children with behavioral or physical predisposing factors. The condition rarely occurs without retention or constipation.
In a child, stool retention and constipation results in dilation of the rectum and sigmoid colon, this is what leads to changes in the reactivity of muscles and nerve of the bowel wall. The changes decrease the efficacy of bowel excretory function leading to further retention. The longer the stool remains in the bowel, the more the water is absorbed, this hardens the stool making passage more. Difficult and painful.
Treatment of fecal incontinence in children involves treating any underlying problem that might be causing constipation. If there is no specific underlying medical condition, you will need to address the symptoms. Initial treatment for fecal incontinence in children will involve educating the parent and child about the physiology of encopresis. This help in removing blame from the child and diffusing the emotional reactions of those involved.
The next step of treatment is relieving any stool impaction, this can be done using a variety of drugs and regiments. The choice for the regiments and drugs will depend on the age of the child and other factors. Behavioral strategies will include structured toilet-sitting times. This can include measures such as having the child sit on the toilet for 5 to 10 minutes after each meal to take advantage of the gastroscopic reflex.
Fecal incontinence after childbirth
Bowel or fecal incontinence to gas are quite common in the first few months after vaginal delivery. During this time, female are also at the risk of developing urinary urgency and incontinence. To determine what the cause of the problems is, a physical examination of the vagina, rectum, anal sphincter muscles and pelvic muscles can is often carried out.
The structure of the pelvic goes through dramatic changes during pregnancy at the time of vaginal childbirth. The pelvic floor, which a collective term for the pelvic muscles that provide support to the pelvic organ, including the vagina (birth canal), the urinary bladder and the rectum that leads to the anus, surrounded by the anal sphincter muscles that control the passage of stool and gas, all undergo dramatic changes.
Most women, especially those having their first vaginal delivery, may experience tearing also called laceration of the vagina or the perineum. These tears are classified y how deep the depth of tissue tear is involved, the laceration can either be:
- First degree tears which involve the skin of the vagina
- Second degree tears involving the skin and a layer of the tissue underneath
- Third degree tearswhich involve the skin, the tissue underneath the skin and the anal sphincter muscles
- Fourth degree tears this will involve all the mentioned layers together with the rectal lining
About half of the women with anal sphincter laceration and repair at delivery will experience some changes related to their bowel control. Women who did not have direct anal sphincter damage May also notice some bowel changes including bowel urgency or incontinence.
Fecal incontinence management
The management of fecal incontinence should be tailored to its clinic manifestation, that is to say, the management should address the treatment of the underlying diseases or medical condition causing the fecal incontinence and should be guided by diagnostic testing.
The management of bowel incontinence may involve the following:
Medical therapy for incontinence
Medical therapy involves conservative treatment option for fecal incontinence. This includes the use of bulking agents and biofeedback. The goal of this therapy of to reduce stool frequency and improve stool consistency.
A regular bowel regimen including laxative should be established. If impacted, manual disimpaction and a daily tap water enema may help prevent reaccumulation.
Surgical therapy
Once medical therapy has been maximized, a minimally invasive and surgical therapy may be considered. Injectable materials may provide an improvement in anal sphincter function. Surgery is in most cases used to correct an underlying problem such as rectal prolapse or sphincter damage, especially after childbirth. Common surgical options will include:
- Sphincteroplasty,which is a surgical procedure to repair damaged or weakened anal sphincter.
- A surgical procedure to treat rectal relapse, a rectocele or hemorrhoids
- Colostomy surgery which diverts stool through an opening in the abdomen.
- Sphincter replacement surgery
- Dynamic graciloplasty,this is an anal sphincter repair surgery
Sacral nerve stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation is a minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of fecal incontinence. A neurostimulator device is used in this procedure to manage fecal incontinence. Also known as sacral neuromodulation, sacral nerve stimulation is a type of electrical stimulation therapy.
The process involves the implantation of a programmable stimulator subcutaneously, the device delivers low amplitude electrical stimulation via a lead to the sacral nerve for the management of fecal incontinence.
Vaginal bowel control device
Like in sacral nerve stimulation, a vaginal bowel control device can be used in women especially after vaginal delivery.
Dietary and pharmacologic management
Dietary and nutritional change is the other best way to manage fecal incontinence. Dietary changes will involve your intake of fiber. You will also need to drink plenty of fluids especially water to remain hydrated. Fiber helps in the absorption of water from the stool.
Pharmacological management of condition such as diarrhea and constipation can also help in the management of bowel incontinence.
Enemas or rectal irrigation
In this process, water is directed into the rectum to clean the bowel of built-up toxins and waste products. Apart from bowel incontinence, enemas or rectal irrigation can also be used in the management of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and constipation
Fecal incontinence treatment
To treatment for fecal incontinence will vary depending on the underlying cause and the pattern of the symptoms. Most health care practitioners will often recommend on less intrusive treatment form first. Those recommended include dietary changes and exercise programmers.
If the above fail to work, then depending on how severe the symptoms are medication may be prescribed. Medication is used to treat soft or loose stools or constipation associated with bowel incontinence this is according to the National Health services, UK.
Loperamide is widely medicine used to treat diarrhea. The medicine works by slowing down the movement of stool through the digestive system, the slow movement allows more water to be absorbed from the stool. The medicine can be prescribed in low doses to be taken regularly over a long period of time.
To treat constipation causing the bowel incontinence, laxatives will be used. Laxatives are a type of medication that helps you pass stool. The most recommended laxative are bulk-forming ones. They help the stool retain fluids, they are less likely to dry out which can lead to fecal impaction.
Here are some of the most recommended treatment option for fecal incontinence:
- Eating the right amount of fiber,this can help both constipation and diarrhea. You can find fiber n fruits, vegetables, whole grain, and beans. Another common source is fiber supplement found in pharmacy and drug stores.
- Drink plenty of fluids most specifically water
- Apart from medication stated above, you can also develop a regular bowel training. Bowel training involves training to have a bowel movement at specific times of the day. Over time, your body becomes used to a regular bowel movement. This might help reduce constipation and related fecal incontinence.
- The other thing is to have pelvic floor exercises and biofeedback. The exercises involve squeezing and relaxing pelvic floor muscles to improve bowel incontinence.
- Surgery may also be an option for fecal incontinence that fails to improve with other treatment. Surgery can also be used for fecal incontinence caused by pelvic floor or anal sphincter muscle injury.
Fecal incontinence pads
Bowel or fecal incontinence can be annoying and quite embarrassing. After using the above mentioned management options for the incontinence, there are available pads that you can wrap yourself in to improve hygiene.
a butterfly pads, and body liners are some of the personal hygiene product that adhere comfortably and discreetly in between the buttocks, providing secure protection for bowel leaks. This pads are available in leading drug stores and pharmacy.
Sources and references
- Causes of fecal incontinence: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/bowel-control-problems-fecal-incontinence
- Fecal incontinence: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fecal-incontinence/symptoms-causes/dxc-20166883
- Bowel incontinence: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Incontinence-bowel/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- What is bowel incontinence: https://www.continence.org.au/pages/faecal-incontinence.html
- Fecal incontinence: http://patients.gi.org/topics/fecal-incontinence/
- 14 possible conditions that could cause fecal incontinence: http://www.healthline.com/symptom/fecal-incontinence
- Fecal incontinence in adults: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cG49
